2019
updated 3/1/2024
Here are 10 Tips for protecting cool season vegetables from freezing temperatures.
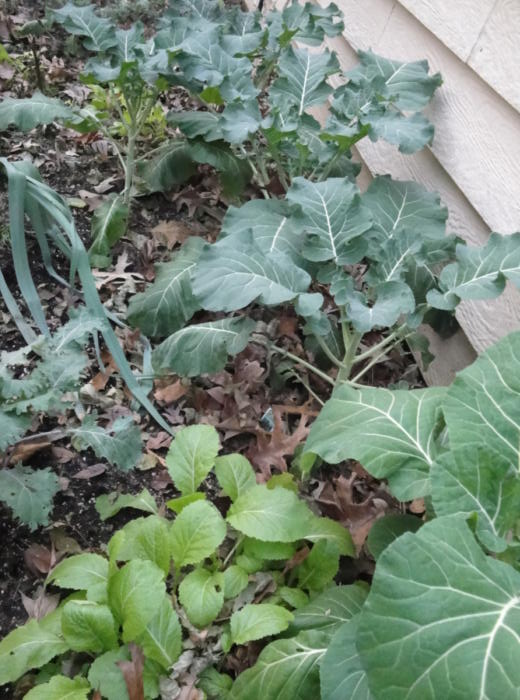

Cool season vegetables: from the top, broccoli, leeks, ‘Red Russian’ kale, light green mustard greens, and collards.
Ready For Fall?
Throughout parts of the United States, and in chilly climates everywhere, gardeners are scrambling to save their tender plants. Most of us have brought in all the houseplants. More laissez-faire gardeners do nothing special to extend the season, beyond harvesting the last of the cherry tomatoes and clearing out the frosted vines.
And there are those of us who strive to keep cool season vegetables growing even in winter. And we’ll plant more of them! Soon I’ll transplant ‘Monstrueux de Viroflay’ spinach seedlings into pots, to grow on the deck through the winter. This French heirloom spinach has huge leaves with a milder flavor. It has lower levels of oxalates, so those who have been advised to avoid eating spinach might be able to eat this variety. Ask your doctor.
In early October, I planted 2 dozen onion sets (for green onions) in a 12″ pot on the deck. Green onions are ready for harvest, in mild weather, only a few weeks after planting the sets. To preserve them in the cold, I’ll cover them with plastic sheeting (Tip #2). Green and bunching onions grow more slowly in cold weather.
I planted more sets every couple of weeks and will soon plant the remaining bulbs before they dry up. A favorite bunching onion called ‘Nabechan’ has straight sides. Not having a bulb at the bottom makes it easier to harvest. Sets are not available for bunching onions, though, so they must be started from seeds.
Where There’s a Will, There’s a Way
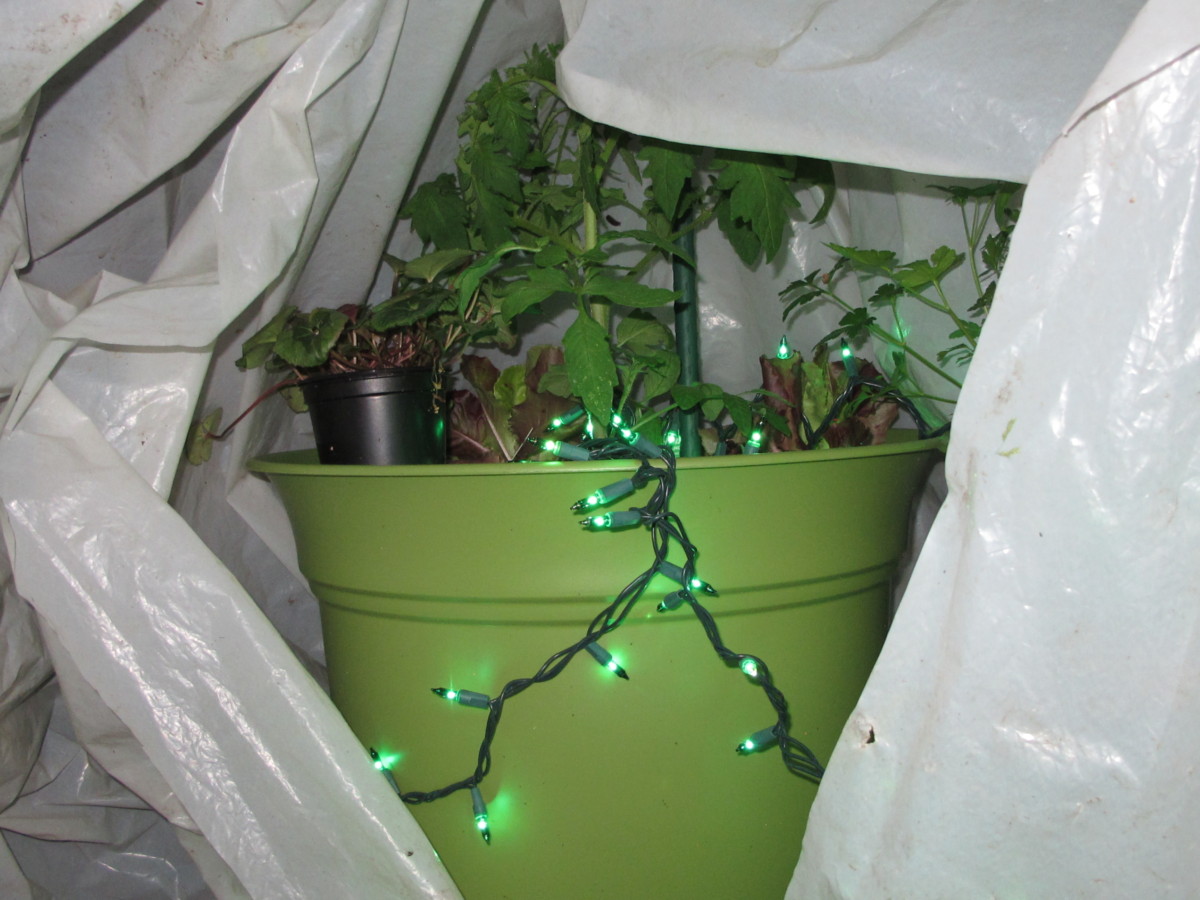
Potted cool season vegetables will grow under a plastic covering in cold weather. To extend the season, strings of miniature incandescent Christmas lights (Tip #6) will raise the temperature to more comfortable levels. Later in this article, I will list all 10 Tips for protecting crops in winter.
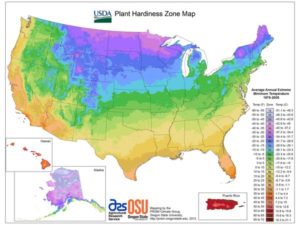
Starting with the simplest ideas and progressing to the more advanced methods, find the level you’re most comfortable with this season. Your budget, your USDA plant hardiness zone (photo, above), and the types of crops themselves must factor into your decision.
As you gain confidence and become more motivated to keep the garden producing, you might decide to try the next level. Cost savings realized by growing your own fresh food might justify the expense of new materials.
It’s only through experimentation, by taking a chance, that you might discover all the opportunities—and the limits—of gardening challenges. This is how green thumbs are cultivated.
If you’ve never grown cool season vegetables, several articles at The Farm In My Yard provide detailed information to get you started. For a greater understanding of any issue, enter the term in the search bar or click it in the tag cloud.
The Advantage of This Latitude
I’ve been growing greens in winter for decades, for my customers and for my family. Fortunately for us, living in the southeast doesn’t present as difficult a winter hardship as would living in Montreal, Montana, or Scotland. But there are options for just about every climate.
There’s no substitute for stepping outside and collecting a green onion, a mild mustard leaf, and some kale and spinach for our Sunday morning omelet. We pick what we need when we need it.
Succession Planting: Warm, Then Cool Season Vegetables
Because our favorite greens love cool weather, they grow in the garden after the tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers have been harvested. So, with some planning, you can schedule a succession of crops. When one crop finishes up, new transplants or seeds are ready to take its place. Now, that’s an efficient use of space!

Cool season vegetables and greens replace summer tomatoes and peppers. Plastic protects plants on very cold nights and the netting deters deer.
Radishes, beets, spinach, and other fast-growing plants can be sown directly into the garden in late summer to early autumn. After they’ve been harvested, there might be time for another quick fall crop.
Certain greens and root vegetables have a shorter window of time during which they retain the best quality. So don’t let them linger in the garden. On the other hand, some cool season vegetables can be harvested over many months of growing! That’s at a time when there are fewer weeds, fewer bugs, and less drought to worry about.
If the weather is still warm for the first round of seeds, look for varieties of cool season vegetables that are more heat tolerant. Some catalogs indicate the preferred soil temperature for each crop, or you can get that information from your agricultural extension office. Soil temperature can be lowered by irrigating during hot weather. Additionally, frames covered with knitted shade cloth, made from black polyethylene (available from Johnny’s Selected Seeds and others), provide consistent shade until the weather cools. That bit of shade can make the difference between seeds germinating in August or having to wait until late September to sow them.
Here in zone 7b (average lowest winter temperatures 5° to 10°F), we enjoy productive edible crops and herbs in the garden year-round…with some protection in winter, of course. But we’ve also grown them in colder Maryland winters.
Because I’ve been “advised” by the HOA to stop growing vegetables in the garden (photo, above), they’re now in pots (photo, below) on the fenced deck. (Note to self: next move, no HOA!) Young ‘Aspabroc’ miniature broccoli plants grow in a 20″ pot, where a tomato grew during in the summer. Italian parsley lasts all winter, and sharp-tipped pine cones discourage squirrels.
***Update***: In October, 2021, after my mother passed away, I moved to a small town in northern North Carolina. More property, more nature, woods in the back (where a bobcat and I came face-to-face!), no traffic, gorgeous topography, great friends, just a couple of degrees cooler than Charlotte, and no HOA to tell me what I must or can’t do on my property. 3/1/2024
Peas…Yummy!
Peas grow best in the garden’s “shoulder seasons”. That’s when temperatures can be cool to warm, and when frost is no surprise. So, before the end of tomato and pepper season, you can sow a pack of pea seeds next to a trellis and begin harvesting two months later.
Edible podded snap peas and snow peas are absolutely delicious. Many are eaten on the spot. And because they grow vertically, the vines take up little square footage. During the shoulder seasons, in moderate climates, they don’t normally require a protective covering.
If you have facilities that can accommodate pea vines, such as a lean-to or a cool greenhouse (Tips #9, #10), this crop can be grown as the temperatures dip lower during the winter months. But there is a point below which the vines will be killed in unheated structures.
Last autumn’s loosely covered pea vines (photo, right) made it just fine through the mild winter and started bearing pods in late winter.
Look for disease resistant varieties when growing any vegetables or greens under cover. Plants are more susceptible to diseases when grown in humid conditions.
Gather Information
Get to know each crop, and how much cold it can tolerate with or without protection from freezing weather. I’ve researched calendars for scheduling vegetables in this zone and have found some of them, compared to my own experience, to be overly conservative. They restrict sowing and transplanting to a narrower period of the calendar than I’m willing to gamble with.
Gardening in a warmer microclimate offers more protection than growing plants out in the open. Planting against a sunny south-facing wall or in a protected corner out of the wind provides opportunities to extend the season.
Kale, collards, spinach, Brussels sprouts, mustard spinach, arugula, leeks, and green onions can tolerate the coldest conditions, within reason. I cover the crops when temperatures dip below the mid 20’s. Even if they’re not covered, they will survive. But I want the plants to continue providing premium quality greens. If not stressed by very low temperatures all day and night, these crops will grow if daytime temperatures rise into the mid 40’s.
Cauliflower and ‘Bright Lights’ Swiss chard need to be covered earlier than other greens. Frost normally won’t kill the plants. But repeated freezing will damage the foliage, halting growth until warmer temperatures (or the protective coverings) return.
These crops and other cool season vegetables won’t need protection if grown farther south. Again, cold tolerance is variety specific, so try new cultivars now and then and see which ones work best for you. For example, ‘Green Magic’ broccoli does well when planted in early spring and again in early autumn. This variety needs a warmer temperature when forming its head. On the other hand, ‘Arcadia’ broccoli can mature in very cold weather, so this is the one I plant later in autumn. Another benefit is ‘Arcadia’s bumper crop of side shoots; in Charlotte, they produced for months.
For More Information
There is so much information online and in catalogs, books, and magazines. But, for local perspectives and information about other growing conditions, check with your agricultural extension office. And speak with helpful vendors at the neighborhood farmers’ market.
Garden clubs, botanical gardens, and garden centers selling seeds, supplies, and transplants sometimes offer classes covering various subjects. My “Cool Season Vegetables and Greens” presentations drew the most attendees. Many of my customers started with just one crop and then returned for more. A healthy addiction!
Keep Records
As you begin new garden projects, place labels with the plants, photograph progress, and take notes for future reference. Add some varieties you’ve never grown before to discover delightful new flavors. Observation of the varieties you’re growing in your garden is invaluable when planning future garden projects. There is no substitute for hands-on experience…and records of successes and failures!
Keeping detailed drawings of crop placement in the garden will help when considering crop rotation. Not growing plants from the same family in the same place every year helps decrease concentrations of pathogens and insects. But, because so many of the cool season vegetables are in the Brassicaceae family, it’s difficult to rotate these crops in our limited space.
Succession planting calls for sequential use of space, maximizing the amount of produce harvested through the seasons. It is especially important to prepare the soil before the fall or spring season, adding fresh compost, aged manure, or planting mix.
For optimal harvests, you’ll need to fertilize regularly as the plants grow. Instead of relying on memory, record the names of the products and when you applied them.
Have all underground utilities marked by your municipality before proceeding and keep a record of their locations. Call 8-1-1 to schedule an appointment.
Headings:
Page 1: Ready For Fall?, Where There’s a Will, There’s a Way (The Advantage Of This Latitude), and Succession Planting: Warm, Then Cool Season Vegetables (Peas, Yummy!, Gather Information)
Page 2: Seed or Transplant? (Seeds, Temperature, Transplants, More Favorites), Crops With Ornamental Edible Leaves (Tender Leaf Kales), Crops That Form Heads, Soil Fertility (The Importance of Microbes), Nutritional Benefits, and Ready For the 10 Tips?
Page 3: Tip #1: Move Tender Plants Indoors, Tip #2: “Quick! Cover Up!”, Tip #3: The Hot Water Bottle, Tip #4: Low Tunnels, Tip #5: Deal with the Wind, Tip #6: Add Christmas Lights, Tip #7: I’ll Have a Double
Page 4: Tip #8: A Simple Cold Frame For Cool Season Vegetables, Tip #9: A Lean-To, Tip #10: The Greenhouse, Finally!
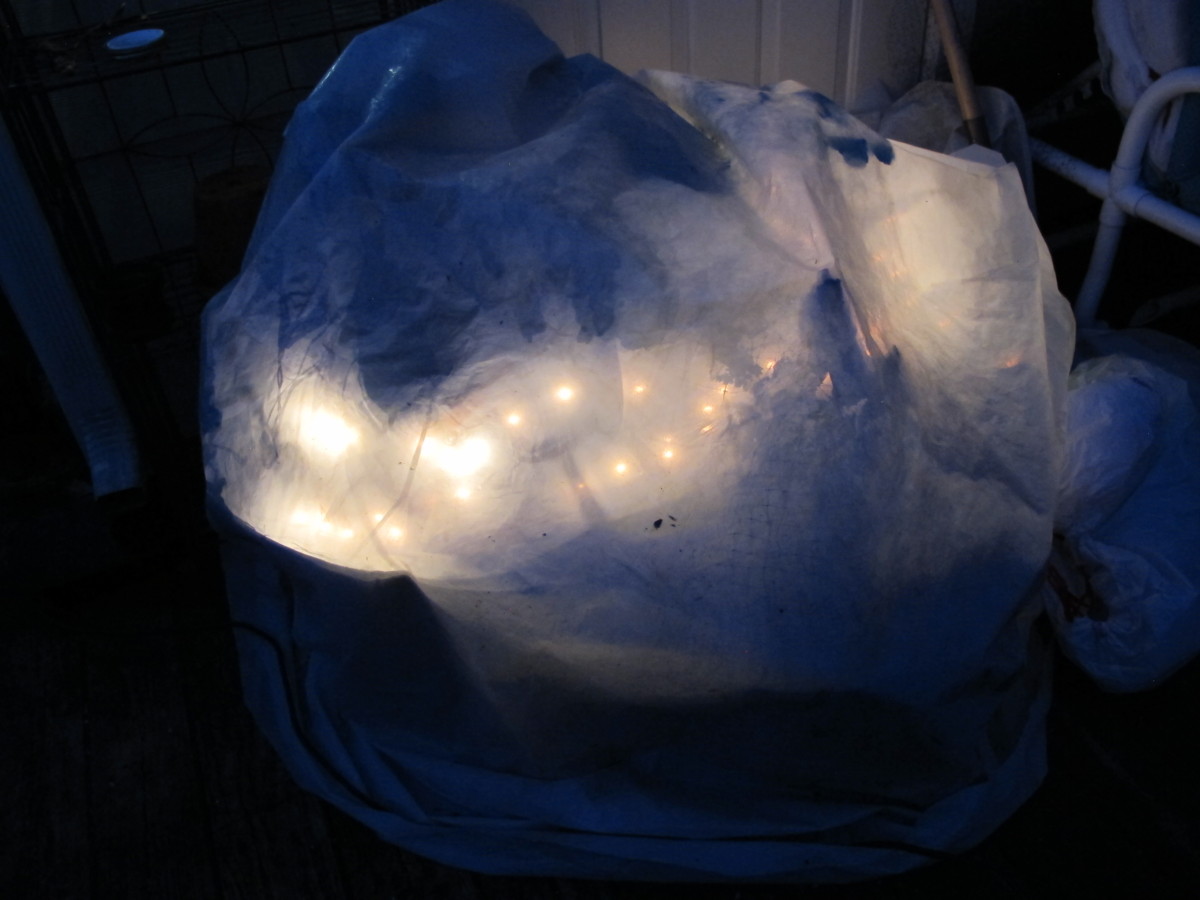










 Since moving to Charlotte, North Carolina (USDA zone 7b/8a) in 2013, I’ve used clear plastic and miniature lights to ripen up the last of the summer vegetables. And they keep cool season greens and vegetables growing through the worst of our winter weather. To avoid any surprises, check the weather forecast daily.
Since moving to Charlotte, North Carolina (USDA zone 7b/8a) in 2013, I’ve used clear plastic and miniature lights to ripen up the last of the summer vegetables. And they keep cool season greens and vegetables growing through the worst of our winter weather. To avoid any surprises, check the weather forecast daily.
 There are few products on the market that demonstrate the phenomenon of planned obsolescence as clearly as cheap imported miniature lights. Stock up on them when they’re plentiful. They don’t last more than a couple of years with frequent use, and they’re becoming increasingly scarce in favor of LED’s. Tread carefully!
There are few products on the market that demonstrate the phenomenon of planned obsolescence as clearly as cheap imported miniature lights. Stock up on them when they’re plentiful. They don’t last more than a couple of years with frequent use, and they’re becoming increasingly scarce in favor of LED’s. Tread carefully!